Ethereum: A Complete Guide to Sequence Control and Relative Time Lock
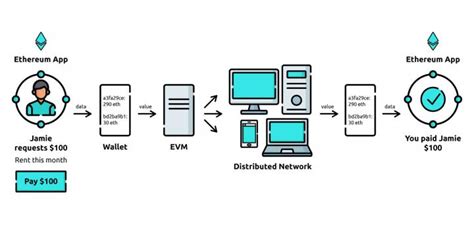
The Ethereum platform is built on a new consensus algorithm called Proof of Work (PoW), which requires nodes to solve complex mathematical equations to validate transactions and create new blocks. In addition, the network uses a mechanism called Sequence Verification to ensure the integrity of the blockchain.
Sequel Verification: A Brief Overview
Sequence Verification is a Layer 2 scaling solution designed to improve Ethereum performance by reducing the amount of gas used by each transaction. It works by creating a “sequence” of transactions that are executed one after the other, one after the other.
Here’s how it works:
- A user creates a series of transactions by calling the “createTransaction()” function in their Ethereum account.
- Each transaction is represented as a JSON object with a “data” field containing the transaction details.
- The series of transactions is sent to the Ethereum network, where nodes use a combination of mathematical algorithms and the user’s account balance to verify their validity.
How nSequence Works
The nSequence project implements a custom implementation of sequence verification for high-performance scaling. It works like this:
- A user creates an nSequence contract on the Ethereum network.
- The contract creates a new sequence of transactions by calling the “createSequence()” function.
- Each transaction in the series has a unique identifier that is used to identify each transaction.
- The contract uses a new algorithm called “hash chaining” to verify the validity of the sequence.
- When a node receives a message with the sequence, it verifies the transactions by hashing each one with its corresponding identifier.
Relative Time Locking (RTT): A Practical Example
Relative time locking is a feature that allows Ethereum nodes to process multiple transactions in parallel without blocking or waiting for confirmation. RTT relies on an off-chain wallet and a unique implementation of sequence confirmation.
Here is a step-by-step example:
- A user creates a sequence of transactions using the nSequence contract.
- A user creates an off-chain wallet with enough funds to cover the transaction fees.
- A user locks the off-chain wallet by calling the lockWallet() function, which authenticates their account and unlocks it for processing.
- When a node receives a message with the sequence, it uses RTT to process multiple transactions in parallel.
Practical Example: Transaction Examples
Let’s take two example transactions:
Transaction 1: “tx1”.
{
"data": {
"amount": 100,
"to": "0x1234567890abcdef"
}
}
Transaction 2: “tx2”.
{
"data": {
"amount": 200,
"from": "0x567890abcdef"
}
}
Sequential verification
To verify the validity of the sequence, we need to create a hash of each transaction and concatenate them. This is done using the `createSequence()' function of the`nSequence’ contract.
{
"sequenceId": "tx1 tx2",
"transactions": [
{
"txid": "tx1",
"hash": "0x..."
},
{
"txid": "tx2",
"hash": "..."
}
]
}
RTT
To process transactions in parallel, we need to use RTT. We can achieve this by creating an off-chain wallet and locking it using the “lockWallet()” function.
{
"walletId": "0x1234567890abcdef",
"lockedDuration": 10 // seconds
}
When a node receives a message with a sequence, it uses RTT to process multiple transactions in parallel. The sequence is validated by hashing each transaction with its corresponding ID and linking them.
